Képgaléria
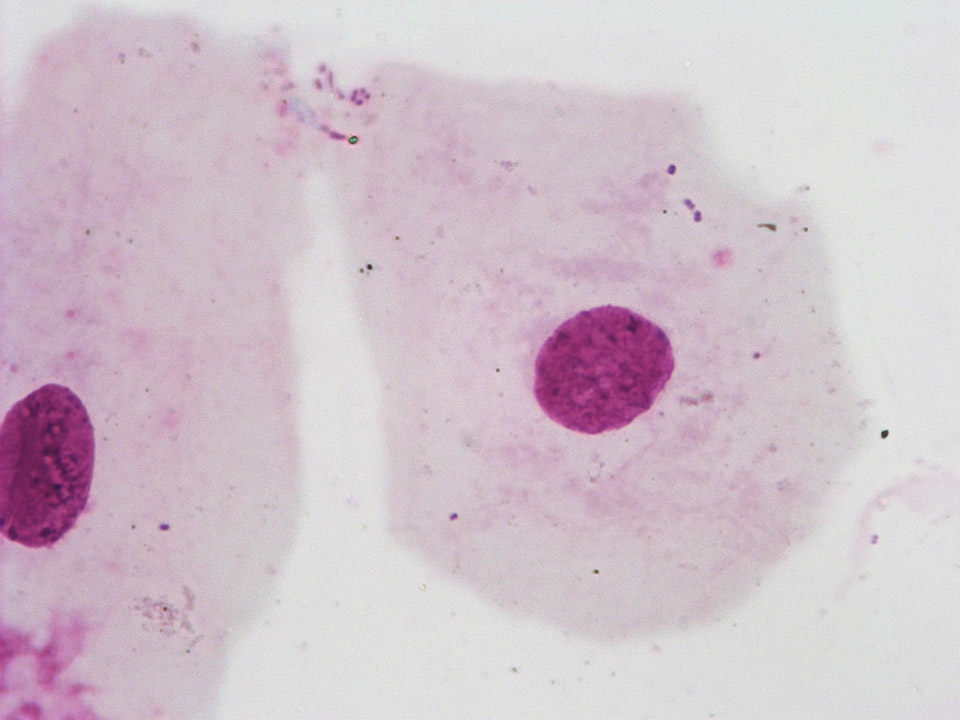
Blood film prepared after storage of the EDTA blood for more than one day. A safe morphological differentiation is no longer possible.
<p>Blood film prepared after storage of the EDTA blood for more than one day. A safe morphological differentiation is no longer possible.</p>
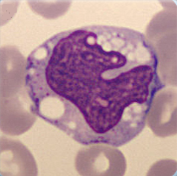
Cell description:
Size: 20 µm
Nucleus: kidney- to band-shaped
Cytoplasm: grey and clear with fine azurophilic granules
They are shortly located in the peripheral blood and then move into the tissue where they differentiate into macrophages. Function: Phagocytosis either of harmful pathogens or dead, dying or damaged cells from the blood.
<p>Cell description: </p> <p>Size: 20 µm </p> <p>Nucleus: kidney- to band-shaped </p> <p>Cytoplasm: grey and clear with fine azurophilic granules </p> <p>They are shortly located in the peripheral blood and then move into the tissue where they differentiate into macrophages. Function: Phagocytosis either of harmful pathogens or dead, dying or damaged cells from the blood. </p>
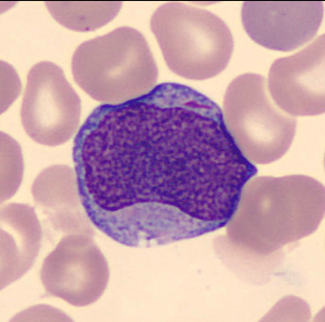
The first microscopically identifiable cell of granulocytic cell line.
Cell description:
Size: 12-20 µm
Nucleus: large, round or slightly oval with diffuse chromatin pattern and often 1-5 nucleoli
Cytoplasm: pale blue and usually agranular, sometimes Auer rods visible
<p>The first microscopically identifiable cell of granulocytic cell line. </p> <p>Cell description: </p> <p>Size: 12-20 µm </p> <p>Nucleus: large, round or slightly oval with diffuse chromatin pattern and often 1-5 nucleoli </p> <p>Cytoplasm: pale blue and usually agranular, sometimes Auer rods visible</p>
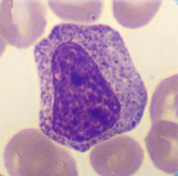
In this maturation stage the separation into the 3 different subpopulations of granulocytes occurs by development of specific granulation for each (secondary granulation).
Cell description:
Size: 10-18 µm
Nucleus: oval or slightly indented with variable degree of chromatin clumping, nucleoli usually not apparent
Cytoplasm: acidophilic neutrophil: primary azurophilic and secondary neutrophilic granules
<p>In this maturation stage the separation into the 3 different subpopulations of granulocytes occurs by development of specific granulation for each (secondary granulation). </p> <p>Cell description: </p> <p>Size: 10-18 µm </p> <p>Nucleus: oval or slightly indented with variable degree of chromatin clumping, nucleoli usually not apparent </p> <p>Cytoplasm: acidophilic neutrophil: primary azurophilic and secondary neutrophilic granules</p>
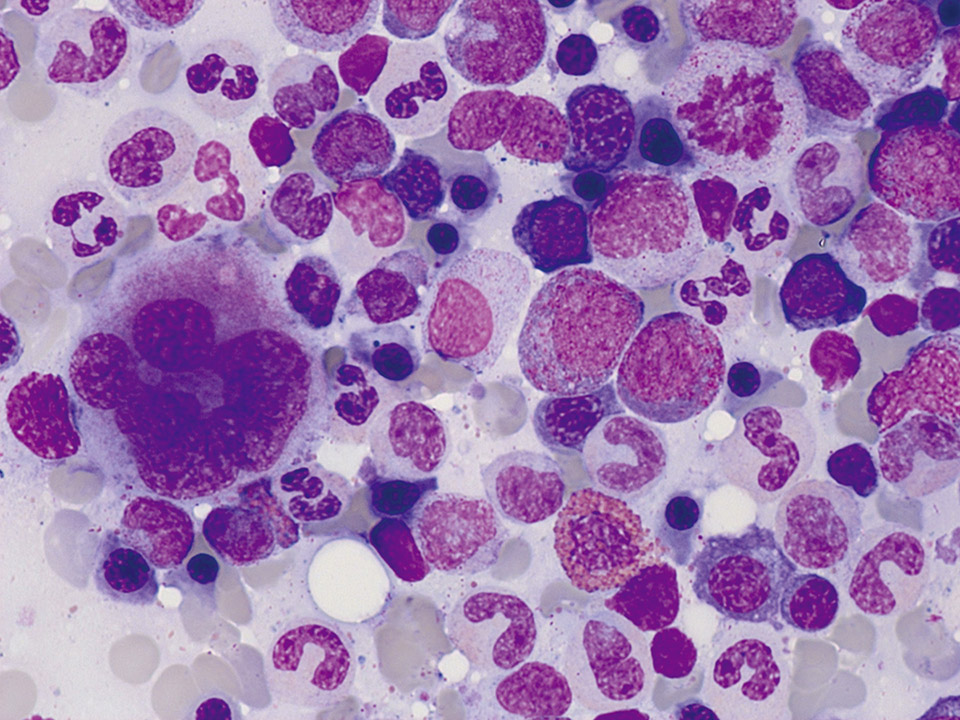
Normal bone marrow cytology. Some cells are always squeezed and damaged. These cells are called smudge cells. Smudge cells cannot be examined and must not be regarded as pathological (They have nothing to do with Gumprecht shadows in the peripheral blood smear). On the top right a mitosis is visible.
<p>Normal bone marrow cytology. Some cells are always squeezed and damaged. These cells are called smudge cells. Smudge cells cannot be examined and must not be regarded as pathological (They have nothing to do with Gumprecht shadows in the peripheral blood smear). On the top right a mitosis is visible. </p>
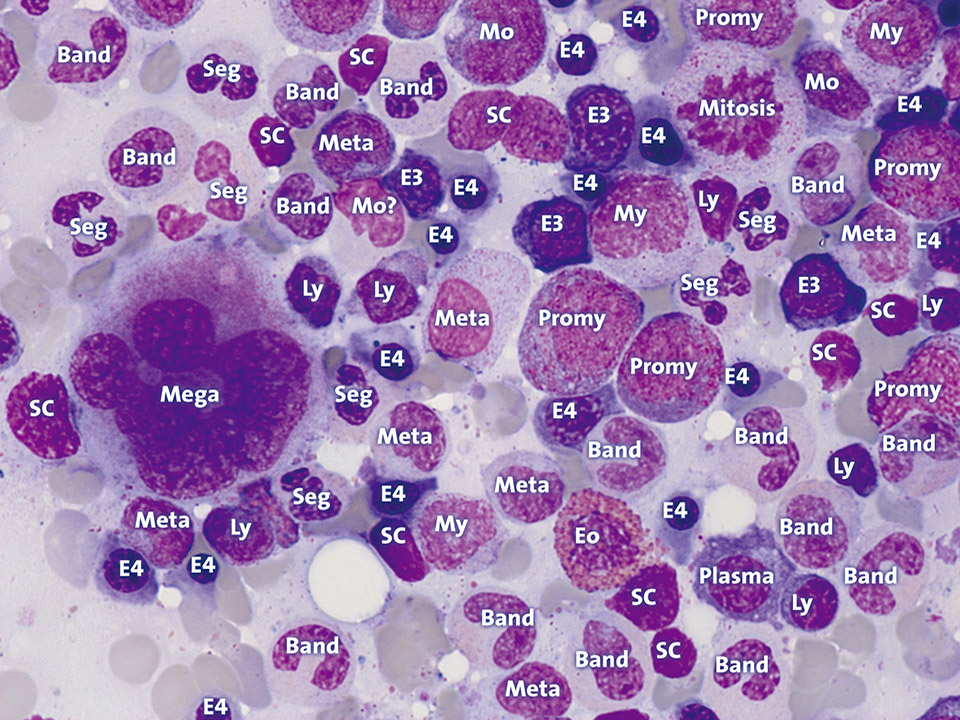
The abbreviations mean: Band: Band neutrophil, E3: Polychromatic erythroblast, E4: Orthochromatic erythroblast, Eo: Eosinophil granulocyte, Ly: Lymphocyte, Mega: Megakaryocyte, Meta: Metamyelocyte, Mo: Monocyte, My: Myelocyte, Plasma: Plasma cell, Promy: Promyelocyte, SC: Smudge cell, Seg: Segmented neutrophil, ?: No clear assignment possible.
<p>The abbreviations mean: Band: Band neutrophil, E3: Polychromatic erythroblast, E4: Orthochromatic erythroblast, Eo: Eosinophil granulocyte, Ly: Lymphocyte, Mega: Megakaryocyte, Meta: Metamyelocyte, Mo: Monocyte, My: Myelocyte, Plasma: Plasma cell, Promy: Promyelocyte, SC: Smudge cell, Seg: Segmented neutrophil, ?: No clear assignment possible.</p>
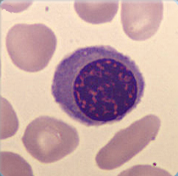
Cell description: 3 different stages of nucleated red blood cells are known: basophilic, polychromatic and orthochromatic
Size: around 10 µm
Nucleus: round with variable degree of chromatin condensation according to maturation, faint or absent nucleoli
Cytoplasm: bluish to pink (depending on maturation), no granules
Nucleus decreases in size as the cell matures
<p>Cell description: 3 different stages of nucleated red blood cells are known: basophilic, polychromatic and orthochromatic </p> <p>Size: around 10 µm </p> <p>Nucleus: round with variable degree of chromatin condensation according to maturation, faint or absent nucleoli </p> <p>Cytoplasm: bluish to pink (depending on maturation), no granules </p> <p>Nucleus decreases in size as the cell matures</p>
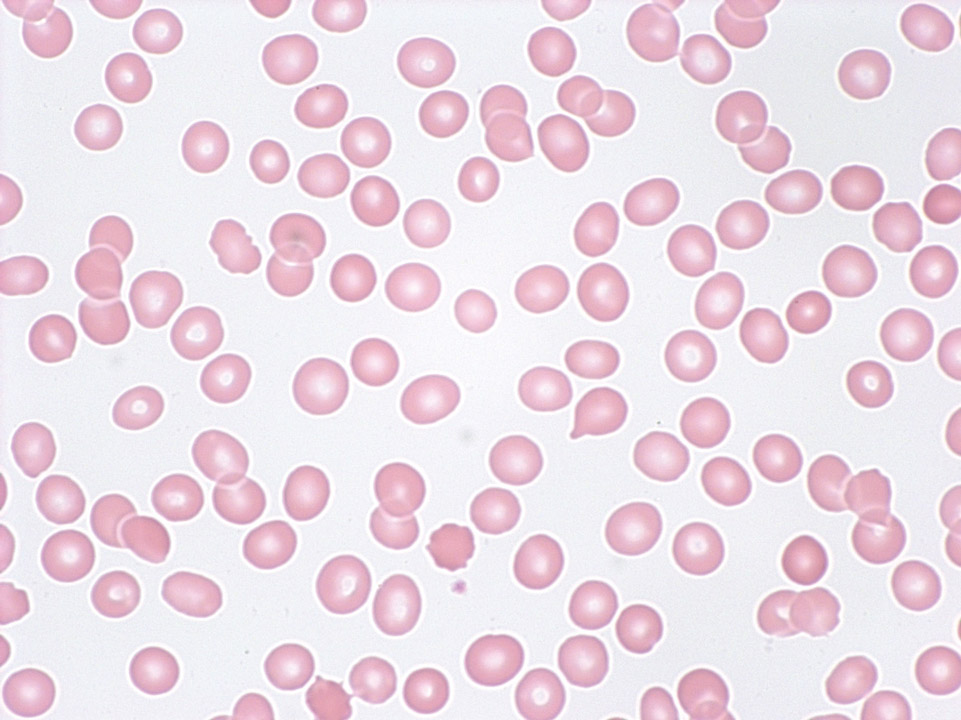
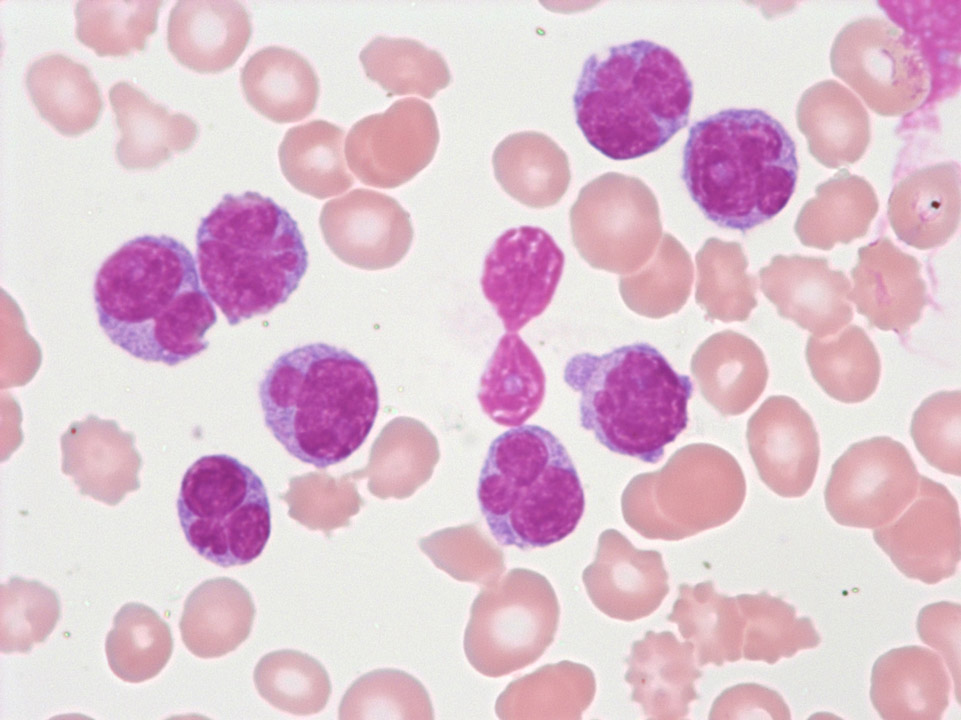
Pancytopenia (tricytopenia) in the peripheral blood (May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain) of a patient with severe aplastic anaemia: The automated cell count showed granulocytopenia (300/µL), mild lymphocytopenia (800/µL), anaemia (haemoglobin 9 g/dL), a reduced reticulocyte count (18,000/µL) and thrombocytopenia (12,000/µL).
<p>Pancytopenia (tricytopenia) in the peripheral blood (May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain) of a patient with severe aplastic anaemia: The automated cell count showed granulocytopenia (300/µL), mild lymphocytopenia (800/µL), anaemia (haemoglobin 9 g/dL), a reduced reticulocyte count (18,000/µL) and thrombocytopenia (12,000/µL).</p>